In today’s hyper-competitive and fast-paced digital economy, organizations are constantly under pressure to innovate, reduce costs, and deliver superior customer experiences. Traditional approaches to process management often fall short, as manual operations can be slow, error-prone, and resource-intensive. This is where Robotic Process Automation (RPA) emerges as a game-changer. By automating repetitive, rules-based tasks, RPA is transforming how businesses operate, allowing them to achieve new levels of efficiency, scalability, and agility.
Understanding RPA: A Brief Overview
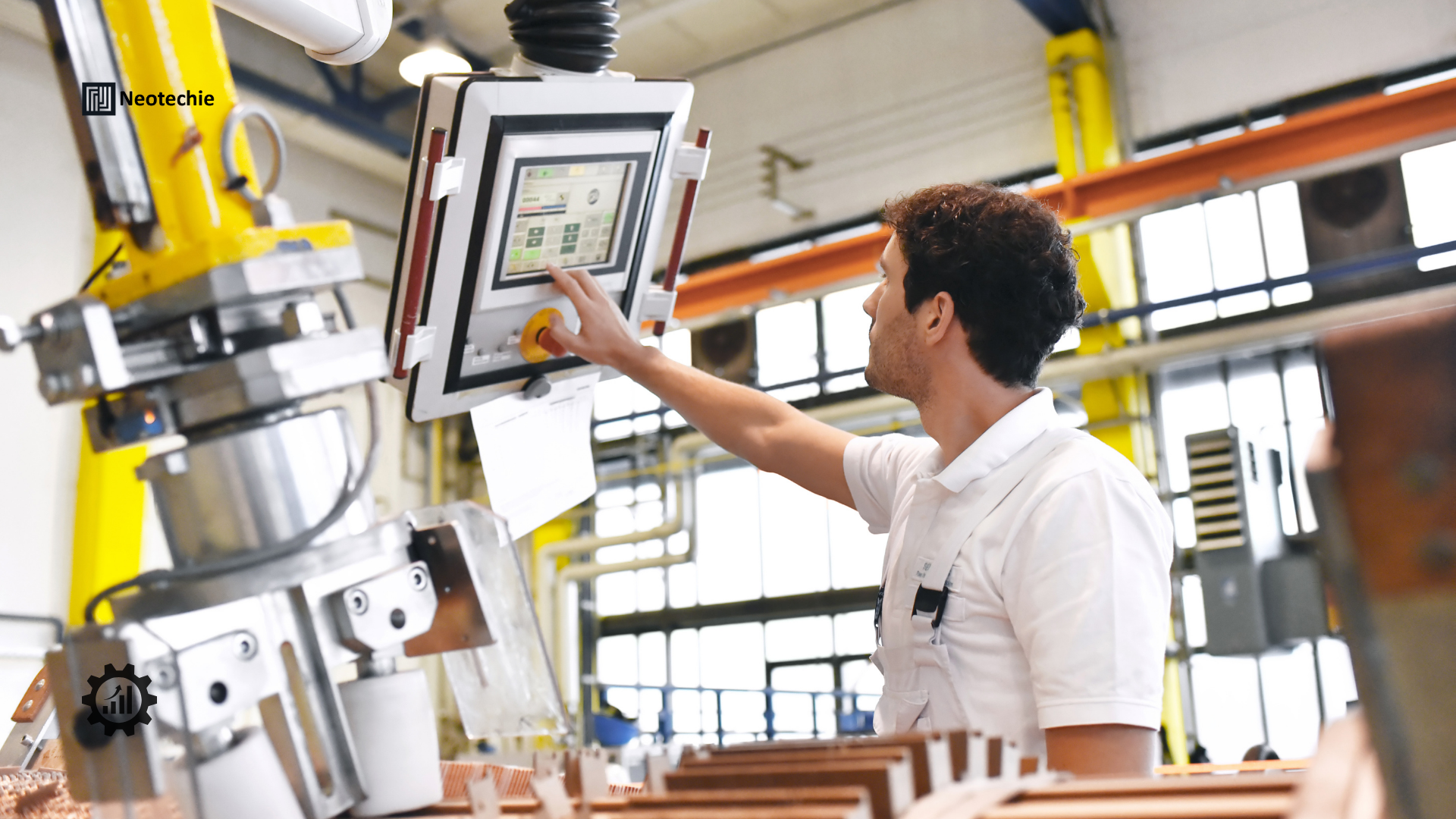
Robotic Process Automation is a technology that uses software robots—or “bots”—to mimic human interactions with digital systems. These bots can log into applications, enter data, process transactions, generate reports, and even communicate with other systems—just as a human worker would, but faster and with near-perfect accuracy. Unlike traditional automation, which often requires extensive system changes, RPA works at the user interface level, making it easier and faster to implement.
The Core Benefits of RPA
The adoption of RPA brings a range of benefits that touch nearly every aspect of a business:
- Efficiency Gains
Bots work around the clock, completing tasks in seconds or minutes that might take humans hours. This enables businesses to handle higher volumes of work without increasing headcount. - Cost Savings
By reducing manual labor, organizations lower operational costs significantly. Many companies report achieving ROI within months of implementation. - Accuracy and Compliance
Human error in repetitive tasks—like data entry or reconciliation—is common. Bots, however, follow exact instructions, ensuring consistency and compliance with regulatory standards. - Employee Satisfaction
By relieving employees of mundane tasks, RPA allows them to focus on higher-value, strategic work, leading to greater engagement and job satisfaction. - Scalability and Agility
Businesses can quickly scale bot operations up or down based on demand, making RPA a flexible solution that grows with the organization.
Industry Applications: RPA in Action
RPA is not limited to a single sector; its versatility allows it to reshape industries across the board:
- Banking and Financial Services: Automates loan approvals, fraud detection, and compliance reporting.
- Healthcare: Streamlines patient onboarding, claims processing, and appointment scheduling.
- Retail and E-Commerce: Enhances order tracking, inventory management, and customer support.
- Manufacturing: Improves supply chain visibility, production scheduling, and quality assurance.
- Government and Public Sector: Simplifies tax administration, public records management, and citizen service delivery.
These use cases demonstrate that RPA is not just about saving time—it’s about enabling businesses to rethink how they deliver value.
Overcoming the Challenges
While RPA offers immense potential, organizations often face challenges in implementation. Common hurdles include:
- Process Suitability: Not all processes are ideal for automation. Processes with high variability or requiring human judgment may resist automation.
- Change Management: Employees may fear job displacement. Clear communication, transparency, and reskilling programs are essential to ease adoption.
- Bot Maintenance: As systems evolve, bots must be updated. Without ongoing governance, automation efforts can quickly break down.
- Scalability: Running a small number of bots is manageable, but orchestrating hundreds or thousands requires robust frameworks and advanced tools.
The key lies in treating RPA not as a quick fix but as part of a broader digital transformation strategy.
RPA as a Strategic Enabler
Beyond cost-cutting, RPA enables organizations to focus on innovation and growth. By automating repetitive processes, companies free up human talent for strategic priorities like product development, customer engagement, and market expansion.
For example:
- A financial institution that automates compliance reporting can redirect skilled analysts to fraud prevention and risk management.
- A healthcare provider using bots for claims processing can allow medical staff to spend more time on patient care.
In this way, RPA acts as a strategic enabler, unlocking capacity and creativity across the organization.
RPA and the Future of Work
The future of RPA lies in its convergence with emerging technologies. When combined with Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML), RPA evolves into Intelligent Automation—capable of handling unstructured data, making decisions, and even learning over time. For example:
- AI-powered bots can process scanned documents or emails.
- ML algorithms can help bots improve accuracy in predicting customer behaviors.
- Natural Language Processing (NLP) enables bots to handle conversational tasks, such as customer queries.
Cloud-based RPA solutions are also gaining momentum, making automation more affordable, scalable, and accessible for businesses of all sizes. This democratization of automation ensures that even smaller organizations can leverage RPA to remain competitive.
The Road Ahead
Looking forward, RPA will become increasingly embedded in business strategies. Organizations that embrace it early will gain a competitive edge by:
- Delivering superior customer experiences through faster, error-free processes.
- Enabling employees to focus on value-driven work.
- Building agile, scalable operations ready for changing market dynamics.
RPA is not just a tool—it’s a catalyst for business transformation. It empowers organizations to bridge the gap between legacy systems and modern digital platforms without the need for expensive overhauls.
Conclusion
Robotic Process Automation is fundamentally changing how businesses function. From streamlining operations to enhancing compliance and empowering employees, RPA is redefining productivity in the digital era. While challenges exist, careful planning, change management, and continuous governance can help organizations unlock its full potential.
By embracing RPA, businesses position themselves not only to survive but to thrive in the evolving digital landscape. It’s not just about doing things faster or cheaper—it’s about doing them smarter.
RPA represents the future of work: agile, intelligent, and human-centric. Organizations that act today will be the ones shaping tomorrow.